Transplant (BMT)
- Description
The primary goal of this quick start guide is to introduce you to the world of Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) and provide a comprehensive overview of this life-saving procedure, including its benefits, risks, and the journey involved. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of BMT as a treatment option for various conditions, the different types of transplants, and the importance of lifelong follow-up care.
This quick start guide also covers essential information about the transplant process, donor selection, and the potential side effects of BMT. By the time you finish, you’ll feel informed and empowered to make informed decisions about your healthcare journey.
Main Features of Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT)
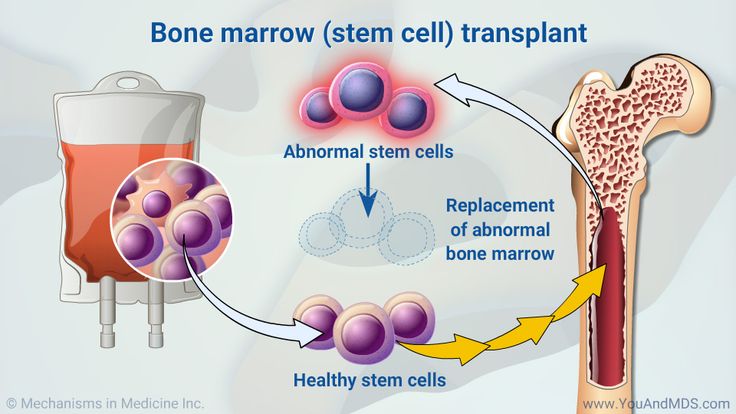
- Replacing Diseased Bone Marrow: BMT is a procedure that replaces diseased or damaged bone marrow with healthy bone marrow cells.
- Treatment for Various Conditions: BMT is used to treat a range of conditions, including:
- Blood cancers: Leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma
- Genetic disorders: Sickle cell anemia, thalassemia
- Autoimmune diseases: Aplastic anemia, severe combined immunodeficiency
- Types of BMT:
- Autologous BMT: Using the patient’s own stem cells collected and stored before treatment.
- Allogeneic BMT: Using stem cells from a matched donor (sibling, unrelated donor, umbilical cord blood).
Benefits of Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Cure for Certain Diseases: BMT can offer a cure for some cancers and genetic disorders.
- Improved Quality of Life: Can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with debilitating blood diseases.
- Restores Normal Blood Cell Production: Replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy cells that can produce normal blood cells.
Risks of Bone Marrow Transplantation
- Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD): Donor cells may attack the recipient’s tissues.
- Infection: Increased risk of infection due to immunosuppression.
- Rejection: The recipient’s body may reject the transplanted bone marrow.
- Side Effects of Conditioning Regimen: High-dose chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy can have significant side effects.
The BMT Journey
- Donor Search and Matching: Identifying a suitable donor through tissue typing and matching.
- Conditioning Regimen: High-dose chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy to prepare the body for the transplant.
- Transplant Procedure: Infusing healthy stem cells into the recipient’s bloodstream.
- Post-Transplant Care:
- Close monitoring for complications, such as infection and GVHD.
- Long-term follow-up care to manage potential side effects and monitor for disease recurrence.
What is the target audience?
- Patients diagnosed with conditions that may be treated with BMT.
- Family members and caregivers of individuals undergoing BMT.
- Healthcare professionals involved in BMT.
- Individuals interested in becoming bone marrow donors.
- The general public seeking information about blood and bone marrow diseases.
Bone Marrow Transplantation is a complex medical procedure with significant risks and benefits. By providing accurate and up-to-date information, this guide aims to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare journey and understand the complexities of this life-saving treatment.